-
 Sarah
Hi there! Welcome to my shop. Let me know if you have any questions.
Sarah
Hi there! Welcome to my shop. Let me know if you have any questions.
Your message has exceeded the limit.

Streamlining Your Manufacturing Process with the Right Tool Storage Solutions
2025-10-29 13:55:54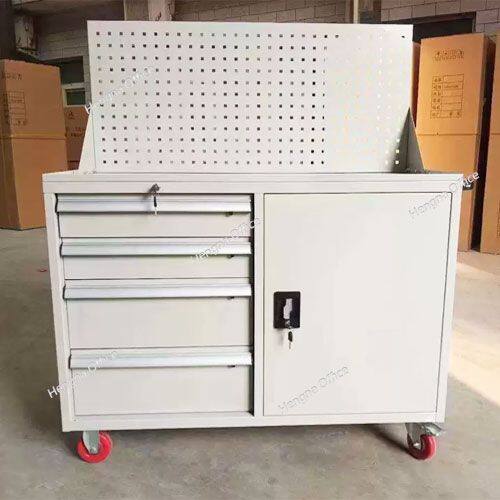
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, manufacturing process improvement has become essential for maintaining market leadership and profitability. One often-overlooked aspect of operational excellence is tool storage solutions – the strategic organization and management of tools that directly impact production efficiency, quality control, and workplace safety. This comprehensive guide explores how the right tool storage systems can transform your manufacturing processes, eliminate bottlenecks, and create a more productive, efficient operation.

The Critical Role of Tool Storage in Manufacturing Excellence
Understanding the Manufacturing Tool Management Challenge
Modern manufacturing facilities face complex tool management challenges that significantly impact operational performance:
Tool accessibility issues: Workers lose valuable production time searching for appropriate tools
Inventory management complexity: Difficulty tracking tool location, condition, and availability
Workflow interruptions: Missing or poorly organized tools disrupting production schedules
Quality control impacts: Using incorrect or poorly maintained tools affecting product quality
Safety concerns: Disorganized tools creating workplace hazards and injury risks
Quantifying the Impact of Inefficient Tool Storage
Industry research reveals compelling statistics about tool storage inefficiencies:
Time loss: Average manufacturing workers spend 12-18 minutes daily searching for tools
Production delays: Tool-related issues cause 15-20% of unscheduled production downtime
Quality costs: Poor tool management contributes to 8-12% of quality-related rework costs
Safety incidents: 25% of workplace injuries involve tool-related accidents
Strategic Tool Storage Solution Implementation
1. Manufacturing Process Analysis and Tool Mapping
Comprehensive Workflow Assessment
Before implementing tool storage solutions, conduct a thorough manufacturing process analysis:
Production Zone Classification
Raw material processing: Tools for cutting, shaping, and initial material preparation
Assembly operations: Equipment for component assembly and sub-assembly production
Quality control stations: Tools for inspection, measurement, and testing procedures
Packaging and finishing: Equipment for final product preparation and shipping
Maintenance areas: Tools for equipment upkeep, repair, and facility maintenance
Tool Usage Pattern Analysis
| Manufacturing Stage | Tool Requirements | Usage Frequency | Storage Priority |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Processing | Cutting tools, measuring devices | Continuous | Critical |
| Assembly Operations | Hand tools, power equipment | High | High |
| Quality Control | Precision instruments, gauges | Regular | Critical |
| Packaging | Sealing tools, labeling equipment | Moderate | Medium |
| Maintenance | Repair kits, diagnostic tools | As needed | Variable |
2. Advanced Tool Storage System Design
Multi-Drawer Configuration Strategy
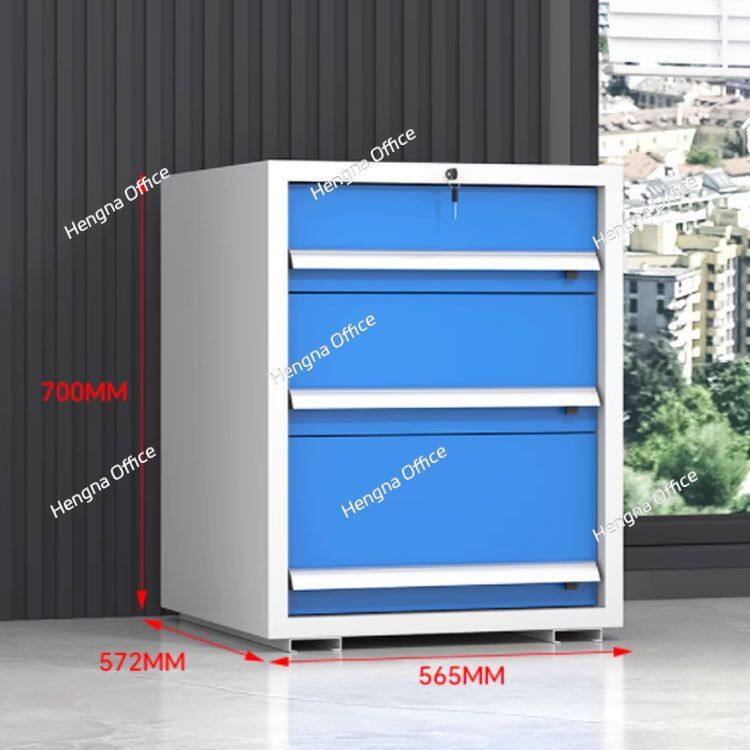
Based on the reference images showing versatile drawer systems, manufacturing tool storage should feature:
Optimal Drawer Organization
Five-drawer systems: Comprehensive categorization accommodating diverse manufacturing tools
Progressive depth configuration: Shallow top drawers (2-3 inches) for small items, deeper bottom drawers (8-12 inches) for bulky equipment
Weight distribution engineering: Heavy tools strategically placed in bottom drawers for stability and safety
Customizable compartment systems: Adjustable dividers adapting to changing manufacturing requirements
Manufacturing-Specific Storage Features
Heavy-duty construction: Steel frames supporting 500-800 lbs of manufacturing tools
Enhanced mobility: Industrial-grade casters navigating manufacturing floor environments
Security integration: Locking systems protecting valuable manufacturing equipment
Environmental protection: Sealed compartments protecting tools from manufacturing contaminants
3. Zone-Specific Tool Storage Solutions
Production Line Integration
Assembly Line Tool Stations
Line-side positioning: Mobile tool carts positioned within arm’s reach of assembly stations
Sequential tool organization: Tools arranged following assembly sequence for optimal efficiency
Quick-change capabilities: Rapid tool swapping supporting product changeovers
Standardized configurations: Consistent setup across multiple assembly lines
Quality Control Areas
Precision tool storage: Specialized compartments for sensitive measuring and testing equipment
Calibration management: Integrated systems tracking tool calibration schedules and status
Clean storage environments: Protected compartments preventing contamination of precision instruments
Documentation integration: Storage for quality control records and testing documentation
Manufacturing Process Optimization Strategies
1. Lean Manufacturing Tool Management
5S Implementation for Tool Storage
Sort (Seiri)
Tool categorization: Systematic organization eliminating unnecessary tools from work areas
Frequency-based placement: Most frequently used tools positioned for immediate access
Redundancy elimination: Removal of duplicate tools and unnecessary equipment
Standardization creation: Consistent tool organization across all manufacturing areas
Set in Order (Seiton)
Designated locations: Specific storage positions for each tool category
Visual management: Clear labeling and color-coding systems for easy identification
Accessibility optimization: Tool placement minimizing movement and search time
Ergonomic arrangement: Tool positioning reducing physical strain and fatigue
Shine (Seiso)
Regular cleaning schedules: Systematic tool and storage maintenance procedures
Inspection integration: Tool condition checking during cleaning processes
Preventive maintenance: Scheduled tool servicing and replacement programs
Continuous improvement: Ongoing optimization of cleaning and maintenance processes
Standardize (Seiketsu)
Consistent procedures: Standardized tool storage and handling protocols
Training programs: Comprehensive education on proper tool management
Documentation systems: Written procedures and visual guides for tool storage
Performance monitoring: Regular audits and compliance checking
Sustain (Shitsuke)
Accountability systems: Individual responsibility for tool storage maintenance
Continuous training: Ongoing education and reinforcement of proper procedures
Performance recognition: Rewards and recognition for tool storage excellence
Regular audits: Scheduled reviews and improvement opportunities
2. Just-in-Time Tool Delivery Systems
Mobile Tool Cart Networks
Automated delivery: Scheduled tool cart movement to production areas as needed
Demand-based positioning: Tool placement based on production schedules and requirements
Real-time availability: Systems showing current tool location and availability status
Quick response capabilities: Rapid tool delivery for urgent production needs
Tool Inventory Management
Real-time tracking: Continuous monitoring of tool location, usage, and condition
Automated reordering: Systems triggering tool replacement when inventory reaches minimum levels
Usage analytics: Data analysis optimizing tool inventory levels and placement
Cost tracking: Detailed monitoring of tool acquisition, maintenance, and replacement costs
Technology Integration for Manufacturing Excellence
1. Smart Tool Storage Systems
IoT-Enabled Manufacturing Solutions
Sensor integration: Tool carts equipped with weight, proximity, and usage sensors
Real-time monitoring: Continuous tracking of tool location, availability, and condition
Predictive maintenance: AI algorithms forecasting tool maintenance needs and replacement timing
Automated alerts: Notifications for tool maintenance, calibration, or replacement requirements
Manufacturing Execution System (MES) Integration
Production scheduling: Tool availability integrated with manufacturing planning systems
Quality control linkage: Tool condition monitoring affecting quality assurance processes
Inventory synchronization: Real-time tool inventory updates across manufacturing systems
Performance analytics: Comprehensive reporting on tool utilization and efficiency impacts
2. Digital Twin Technology
Virtual Tool Management
Digital modeling: Virtual representations of physical tool storage systems
Simulation capabilities: Testing different tool organization strategies before implementation
Optimization algorithms: AI-powered systems suggesting optimal tool placement and organization
Predictive analysis: Forecasting tool needs based on production schedules and requirements
Measuring Manufacturing Process Improvement
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Efficiency Metrics
| Performance Indicator | Before Implementation | After Implementation | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tool Search Time | 10-15 minutes per task | 1-2 minutes per task | 85% reduction |
| Production Downtime | 4.5 hours per week | 1.5 hours per week | 67% reduction |
Changeover Time | 45 minutes | 25 minutes | 44% reduction |
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) | 72% | 85% | 18% increase |
Quality Improvements
Defect reduction: 25-35% decrease in tool-related quality issues
Rework costs: 40-50% reduction in rework expenses
Customer satisfaction: 15-20% improvement in quality-related customer satisfaction
Compliance rates: 95%+ achievement of quality standards and specifications
Financial Impact Analysis
Revenue Enhancement
Increased production capacity: 20-30% improvement in daily output volume
Reduced changeover time: 40-50% faster product changeovers increasing flexibility
Improved quality: Higher first-pass yield reducing scrap and rework costs
Enhanced customer satisfaction: Improved on-time delivery and quality performance
Cost Reduction Benefits
Labor efficiency: 25-35% improvement in worker productivity
Tool management costs: 50-60% reduction in tool replacement and maintenance expenses
Quality cost savings: 30-40% reduction in quality-related expenses
Safety improvements: 60-70% reduction in tool-related workplace incidents
Implementation Best Practices
1. Phased Implementation Strategy
Pilot Program Approach
Area selection: Choose one manufacturing area for initial implementation
Baseline measurement: Document current performance metrics and tool management challenges
Solution implementation: Deploy tool storage systems in pilot area
Results evaluation: Measure improvements and identify optimization opportunities
Full-Scale Rollout
Learnings application: Apply pilot program insights to facility-wide implementation
Training reinforcement: Comprehensive education for all manufacturing personnel
System integration: Ensure compatibility with existing manufacturing systems
Continuous improvement: Ongoing optimization based on performance data
2. Change Management Excellence
Employee Engagement Strategies
Stakeholder involvement: Include manufacturing employees in selection and design processes
Benefits communication: Clear explanation of improvements and advantages
Training programs: Comprehensive education on new tool storage systems
Feedback mechanisms: Regular input collection and system refinement
Tags: Streamlining Your Manufacturing Process, Right Tool Storage Solutions, Tool Storage

